TPM
- Home
- TPM
Total Productive Maintenance

It has been developed from the original PM (Preventive Maintenance) concept and methodology. TPM is now rapidly becoming a method applied worldwide and is established as a renowned cultural improvement programme.
TPM drives and delivers world-class performance in production and maintenance and helps close the productivity and quality gap.
TPM is a holistic approach to equipment maintenance that strives to achieve perfect production with little or no breakdowns, no short stoppages and no defects. It promotes a safe working environment with no accidents. TPM emphasises proactive and preventive maintenance practices to maximise the operational efficiency of equipment and places a strong emphasis on empowering operators to maintain equipment to a high standard.
TPM is effective in improving productivity by increasing availability, reducing cycle times and achieving zero defects.
The Pillar Approach:
The pillar approach is a way of managing change and a rigorous methodology to ensure results and improvements are sustained. The mission of each pillar is to reduce loss with the ultimate aim of elimination of all losses.
How is the ‘Pillar’ implemented?
The pillar follows a structured set of steps aligned with the Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) cycle, which can be implemented for improvement activities of any size or complexity in any organisation.
The pillar builds an understanding and analysis of the different loss types affecting an organisation.
The pillar operates at a strategic level, identifying the criteria for project selection and TPM deployment that will deliver the business objectives.
Why is TPM implemented?
These are three of the main drivers for ‘why do’ TPM.
- 1. Company’s increasing reliance and dependency on complicated, high tech, expensive capital equipment. Possibly with no alternative routing if downtime occurs resulting in lost production/profit.
- 2. Because the equipment is increasingly more expensive it pays to recognise what can be done to extend the life cycle, through sound TPM methods, rather than a premature costly replacement.
- 3. By improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), rather than basic up and downtime measures, is a more refined method of monitoring asset management.
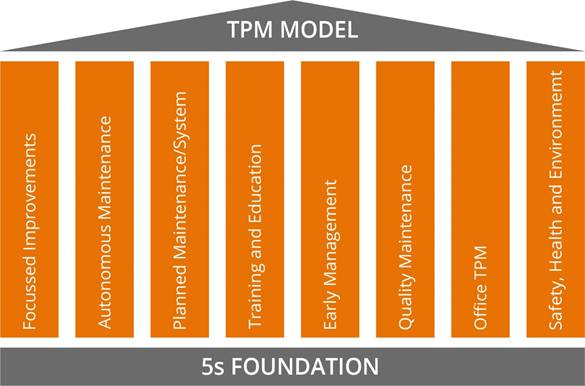
To start the implementation of TPM senior management need to understand that TPM needs to be part of a long-term culture change programme, not just an initiative for the maintenance department. A TPM structure to support the cultural change needs definition with clear responsibilities and ownership.
TPM Aims at
1. Establishing a corporate culture that will maximize production system effectiveness,
2. Organizing a “genba-gembutsu” system to prevent losses and achieve such “reduction-to-zero” targets as “zero-accidents”, “zero-defects” and “zero-breakdowns” in the entire production system life-cycle,
3. Involving all functions of an organization including production, development, sales and management,
4. Involving every member of an organization, from top management to front-line operators, and
5. Achieving zero losses through the activities of overlapping small groups.
Our TPM consultants engage all levels and function in an organization to maximize overall production efficiency besides tuning up existing processes and equipment by reducing mistakes and accidents.
Our TPM consultants ensure that while the maintenance department remains the key holder for preventive maintenance, it is not restricted to the department and involve workers in all department and levels to ensure effective equipment operation.
A vital part of our Total Productive Maintenance consulting is to train workers to take care of the equipment with which they work.
Our Total Productive Maintenance consulting is directed towards the ultimate goal of zero equipment breakdown and zero product defects, which in turn results in improved utilization of production assets and plant capacity.
For further details please contact us